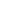
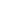
This limits maximum speed because the wheels slip when moving too fast.
The maglev concept overcomes this limitation by levitating the train above the track.
-
This system also resolves issues below.
- Noise
- Power feeding

The Superconducting Maglev system is actually based on a very common motor principle.
The term "linear motor" comes from the fact that motors are lined up linearly.
The Superconducting Maglev system is actually based on a very
common motor principle. The term "linear motor" comes
from the fact that motors are lined up linearly.

Its electrical resistance generates heat, wasting energy.
repel one another, levitating the train by about 3.9 in. and propelling it forward.
guideway attract and repel one another, levitating the
train by about 3.9 in. and propelling it forward.

Coils" turning into magnets when other magnets come close.
When superconducting magnets on vehicle pass by the Levitation
and Guidance Coils at high speed, electric current runs through the
Levitation and Guidance coils, generating magnetic force and
levitating and maintaining the train at a height where the train's
weight is balanced against the magnetic force.
(Levitation height: about 3.9in.)
There is no need to feed electricity to the Levitation and Guidance
Coils to achieve train levitation.

Even when the vehicle leans closer to one side, the magnetic force
that acts between superconducting magnets and the Levitation and
Guidance Coils keep the train centered in the guideway at all times.
The magnetic force prevents the Superconducting Maglev from
crashing into guideway walls and contributes to stable operation.



The motor uses magnetic force to convert electricity to rotation. Attractive forces between north and south poles, and repulsive forces between S-S and N-N poles, power the train.

A linear motor is like a conventional rotating motor that is opened up and extended linearly. It uses magnetic action to drive a train.

A permanent magnet is a magnetized material that creates a continuous magnetic field.

1. It requires electric current to act as a magnet.
2. Its N and S poles can be switched by changing the direction of electric current.